Electricity Generation Forecast using ANN with R, Dr. Arunachalam Rajagopal
Electricity Generation Forecast using Artificial Neural Network with R
Arunachalam Rajagopal
The artificial
neural network (ANN) is based on the concept of machine learning. ANN attempts
to mimic the human brain into the machine (computer). ANNs attempt to learn the
patterns that are exhibited in the training dataset (input - independent
variable and output - dependent variable). Then based on the previous learning,
ANN attempts to give generalized solution for the total dataset. The solution
could be forecast in a time series dataset or causal regression model. It could
also be used for classification of the dataset like what is done in a
discriminant analysis or logistic regression.
Artificial
neural network (ANN) are data-driven and self-adaptive.
There is no need to make any a priori assumption on the input data. The neural
network model is formed in an adaptive manner based on the pattern exhibited by
the dataset. The artificial neural network is basically non-linear in contrasts
to the linear regression models including ARIMA models. This makes it more
adaptive to different kinds of dataset and the predictions are mostly more
accurate than the other models of forecasting or classification models
ANN
Architecture:
The most widely
used ANN architecture is based on multilayer perceptron (MLP). MLP in general
comprises of input layer, single hidden layer, and output layer. There could
also be more than one hidden layer also. The nodes in the various layers are
known as processing elements. The elements in the input, hidden, and output
layers are connected by acyclic links. Each link is associated with a weight.
The most commonly used ANN architecture consists of three layers: input layer, a
single hidden layer, and an output layer. The network works on the principle of
feed forward network (FNN) mechanism.
Yk = pi_out (alpha_k + sum over h (Whk * pi_h ( alpha_h + sum over i (
Wih * Xi))))
where,
W = weight
associated with each link in the network
i = number of
inputs
h = number of
elements in the hidden layer
k = number of
outputs
The activation
function pi_h of the hidden layer is taken to be
logistic function; pi_out is activation function at
the output level; alpha_h and alpha_k are bias coefficients.
f(z) = exp(z)/(1 + exp(z))
A)
Electricity generation forecasting:
The dataset for
forecasting comprises of data starting from 1960-61 to 2018-19. The response
variable is electricity generated in billion units (billion kwh). The regressor or the
independent variables are gdp in billions of rupees
and population in million. The following R-code has been made use of making
forecast of electricity generation in billion kwh for
the next 10 years. The neural network diagram has been plotted using 'NeuralNetTools' package and is shown in Figure 1. The file
‘bnkwh_gdp.csv’ holds the dataset for this example.
> #R
code:
> abc <- read.csv("bnkwh_gdp.csv",
sep=",", header=TRUE)
> head(abc)
year pop_mn gdp_bn gdp_pcap bn_kwh
1 1960-61 434 178.70 411.75 16.94
2 1961-62 444 189.12 425.95 20.15
3 1962-63 454 203.21 447.60 23.36
4 1963-64 464 233.50 503.23 26.57
5 1964-65 474 272.22 574.30 29.78
6 1965-66 485 286.93 591.61 32.99
> kwhgdp<-data.frame(abc[,c(2,3,5)])
> kwhgdp
pop_mn
|
gdp_bn
|
bn_kwh
| |
1
|
434
|
178.70
|
16.94
|
2
|
444
|
189.12
|
20.15
|
3
|
454
|
203.21
|
23.36
|
4
|
464
|
233.50
|
26.57
|
5
|
474
|
272.22
|
29.78
|
6
|
485
|
286.93
|
32.99
|
7
|
495
|
324.39
|
37.81
|
8
|
506
|
380.03
|
42.62
|
9
|
518
|
402.57
|
47.43
|
10
|
529
|
443.34
|
51.62
|
11
|
541
|
473.54
|
55.80
|
12
|
554
|
507.08
|
59.43
|
13
|
567
|
559.12
|
63.06
|
14
|
580
|
680.95
|
66.69
|
15
|
593
|
804.79
|
72.94
|
16
|
607
|
864.52
|
79.20
|
17
|
620
|
931.89
|
85.30
|
18
|
634
|
1056.15
|
91.40
|
19
|
648
|
1144.91
|
102.52
|
20
|
664
|
1258.82
|
104.70
|
21
|
679
|
1499.87
|
120.80
|
22
|
692
|
1758.45
|
122.10
|
23
|
708
|
1960.10
|
130.30
|
24
|
723
|
2280.77
|
140.20
|
25
|
739
|
2551.87
|
156.86
|
26
|
755
|
2880.95
|
170.40
|
27
|
771
|
3221.44
|
187.70
|
28
|
788
|
3655.92
|
202.10
|
29
|
805
|
4323.97
|
221.40
|
30
|
822
|
4961.97
|
245.44
|
31
|
839
|
5786.67
|
264.30
|
32
|
856
|
6637.98
|
287.03
|
33
|
872
|
7629.00
|
301.40
|
34
|
892
|
8792.75
|
324.00
|
35
|
910
|
10325.07
|
350.40
|
36
|
928
|
12132.41
|
380.00
|
37
|
946
|
14061.95
|
395.89
|
38
|
964
|
15591.89
|
421.70
|
39
|
983
|
17884.10
|
448.50
|
40
|
1001
|
20076.99
|
480.70
|
41
|
1019
|
21546.80
|
499.50
|
42
|
1040
|
23357.77
|
517.44
|
43
|
1056
|
25196.37
|
532.70
|
44
|
1072
|
28207.95
|
565.10
|
45
|
1089
|
32198.35
|
594.40
|
46
|
1106
|
36672.53
|
623.80
|
47
|
1122
|
42614.72
|
670.65
|
48
|
1138
|
49665.78
|
723.00
|
49
|
1154
|
55971.40
|
741.20
|
50
|
1170
|
64398.27
|
799.80
|
51
|
1186
|
77023.08
|
844.80
|
52
|
1202
|
89328.92
|
923.20
|
53
|
1217
|
98345.81
|
964.50
|
54
|
1239
|
111328.77
|
1014.80
|
55
|
1254
|
123407.72
|
1048.40
|
56
|
1324
|
135226.56
|
1090.85
|
57
|
1350
|
149941.09
|
1135.33
|
58
|
1354
|
166275.85
|
1206.31
|
59
|
1369
|
190100.00
|
1249.34
|
> scalemin<-apply(kwhgdp,2,min)
> scalemax<-apply(kwhgdp,2,max)
> scaledata<-data.frame(scale(kwhgdp, center=scalemin, scale=scalemax-scalemin))
> scaledata
pop_mn
|
gdp_bn
|
bn_kwh
| |
1
|
0.000000000
|
0.000000000
|
0.000000000
|
2
|
0.010695190
|
0.000054865
|
0.002604674
|
3
|
0.021390370
|
0.000129054
|
0.005209348
|
4
|
0.032085560
|
0.000288541
|
0.007814021
|
5
|
0.042780750
|
0.000492415
|
0.010418695
|
6
|
0.054545450
|
0.000569868
|
0.013023369
|
7
|
0.065240640
|
0.000767107
|
0.016934437
|
8
|
0.077005350
|
0.001060071
|
0.020837390
|
9
|
0.089839570
|
0.001178751
|
0.024740344
|
10
|
0.101604280
|
0.001393419
|
0.028140214
|
11
|
0.114438500
|
0.001552433
|
0.031531970
|
12
|
0.128342250
|
0.001729032
|
0.034477442
|
13
|
0.142245990
|
0.002003040
|
0.037422915
|
14
|
0.156149730
|
0.002644516
|
0.040368387
|
15
|
0.170053480
|
0.003296576
|
0.045439792
|
16
|
0.185026740
|
0.003611075
|
0.050519312
|
17
|
0.198930480
|
0.003965801
|
0.055469004
|
18
|
0.213903740
|
0.004620072
|
0.060418695
|
19
|
0.228877010
|
0.005087423
|
0.069441740
|
20
|
0.245989300
|
0.005687198
|
0.071210646
|
21
|
0.262032090
|
0.006956408
|
0.084274586
|
22
|
0.275935830
|
0.008317919
|
0.085329438
|
23
|
0.293048130
|
0.009379675
|
0.091983122
|
24
|
0.309090910
|
0.011068110
|
0.100016228
|
25
|
0.326203210
|
0.012495540
|
0.113534567
|
26
|
0.343315510
|
0.014228260
|
0.124521259
|
27
|
0.360427810
|
0.016021060
|
0.138558909
|
28
|
0.378609630
|
0.018308740
|
0.150243427
|
29
|
0.396791440
|
0.021826250
|
0.165903927
|
30
|
0.414973260
|
0.025185540
|
0.185410581
|
31
|
0.433155080
|
0.029527860
|
0.200714054
|
32
|
0.451336900
|
0.034010300
|
0.219157741
|
33
|
0.468449200
|
0.039228350
|
0.230817916
|
34
|
0.489839570
|
0.045355890
|
0.249156118
|
35
|
0.509090910
|
0.053424080
|
0.270577735
|
36
|
0.528342250
|
0.062940330
|
0.294595910
|
37
|
0.547593580
|
0.073100020
|
0.307489451
|
38
|
0.566844920
|
0.081155670
|
0.328432327
|
39
|
0.587165780
|
0.093224930
|
0.350178513
|
40
|
0.606417110
|
0.104771200
|
0.376306394
|
41
|
0.625668450
|
0.112510300
|
0.391561181
|
42
|
0.648128340
|
0.122045700
|
0.406118143
|
43
|
0.665240640
|
0.131726500
|
0.418500487
|
44
|
0.682352940
|
0.147583500
|
0.444790652
|
45
|
0.700534760
|
0.168594300
|
0.468565401
|
46
|
0.718716580
|
0.192152400
|
0.492421292
|
47
|
0.735828880
|
0.223440000
|
0.530436547
|
48
|
0.752941180
|
0.260566200
|
0.572914638
|
49
|
0.770053480
|
0.293767500
|
0.587682571
|
50
|
0.787165780
|
0.338137800
|
0.635232068
|
51
|
0.804278070
|
0.404611700
|
0.671746186
|
52
|
0.821390370
|
0.469406100
|
0.735361895
|
53
|
0.837433160
|
0.516883100
|
0.768873742
|
54
|
0.860962570
|
0.585242800
|
0.809688413
|
55
|
0.877005350
|
0.648842500
|
0.836952288
|
56
|
0.951871660
|
0.711072700
|
0.871397274
|
57
|
0.979679140
|
0.788549700
|
0.907489451
|
58
|
0.983957220
|
0.874557800
|
0.965084388
|
59
|
1.000000000
|
1.000000000
|
1.000000000
|
> set.seed(123)
> library(nnet)
> library(NeuralNetTools)
> kwh_nn <- nnet(bn_kwh ~ gdp_bn + pop_mn, scaledata, size = 5, decay
= 1e-3, linout = T, skip = F, maxit = 1000, Hess = T)
# weights: 21
initial value
7.652763
iter 10 value 0.029795
iter 20 value 0.026070
iter 30 value 0.024238
iter 40 value 0.023878
iter 50 value 0.023284
iter 60 value 0.022457
……………………………………
iter 250 value 0.019137
iter 260 value 0.019133
iter 270 value 0.019133
iter 280 value 0.019132
iter 290 value 0.019132
iter 300 value 0.019132
final value 0.019132
converged
> summary(kwh_nn)
a 2-5-1 network with 21 weights
options were - linear output units decay=0.001
b->h1 i1->h1
i2->h1
0.02
0.12
-0.16
b->h2 i1->h2
i2->h2
1.41 -1.53
-2.24
b->h3 i1->h3
i2->h3
0.02
0.12
-0.16
b->h4 i1->h4
i2->h4
-0.19
0.43
-1.02
b->h5 i1->h5
i2->h5
0.02
0.12
-0.16
b->o h1->o
h2->o h3->o h4->o h5->o
0.35 0.31 -1.62 0.31
1.05 0.31
> plotnet(kwh_nn)
> ycap <-
fitted.values(kwh_nn)*(max(kwhgdp$bn_kwh)-min(kwhgdp$bn_kwh))+min(kwhgdp$bn_kwh)
> bnkwh<-data.frame(actualbnkwh=kwhgdp$bn_kwh, fittedbnkwh=ycap[,1])
Figure 1 Neural network diagram
> bnkwh
actualbnkwh
|
fittedbnkwh
| |
1
|
16.94
|
4.92
|
2
|
20.15
|
8.53
|
3
|
23.36
|
12.26
|
4
|
26.57
|
16.17
|
5
|
29.78
|
20.22
|
6
|
32.99
|
24.71
|
7
|
37.81
|
29.01
|
8
|
42.62
|
33.92
|
9
|
47.43
|
39.29
|
10
|
51.62
|
44.45
|
11
|
55.80
|
50.17
|
12
|
59.43
|
56.57
|
13
|
63.06
|
63.23
|
14
|
66.69
|
70.37
|
15
|
72.94
|
77.71
|
16
|
79.20
|
85.55
|
17
|
85.30
|
93.07
|
18
|
91.40
|
101.60
|
19
|
102.52
|
110.20
|
20
|
104.70
|
120.35
|
21
|
120.80
|
130.69
|
22
|
122.10
|
140.08
|
23
|
130.30
|
151.37
|
24
|
140.20
|
162.79
|
25
|
156.86
|
174.92
|
26
|
170.40
|
187.56
|
27
|
187.70
|
200.51
|
28
|
202.10
|
214.87
|
29
|
221.40
|
230.57
|
30
|
245.44
|
246.40
|
31
|
264.30
|
263.36
|
32
|
287.03
|
280.68
|
33
|
301.40
|
298.08
|
34
|
324.00
|
319.73
|
35
|
350.40
|
341.75
|
36
|
380.00
|
365.27
|
37
|
395.89
|
389.52
|
38
|
421.70
|
411.92
|
39
|
448.50
|
438.89
|
40
|
480.70
|
464.53
|
41
|
499.50
|
486.61
|
42
|
517.44
|
512.71
|
43
|
532.70
|
534.66
|
44
|
565.10
|
561.97
|
45
|
594.40
|
594.35
|
46
|
623.80
|
628.45
|
47
|
670.65
|
667.76
|
48
|
723.00
|
711.02
|
49
|
741.20
|
749.76
|
50
|
799.80
|
796.10
|
51
|
844.80
|
857.26
|
52
|
923.20
|
913.66
|
53
|
964.50
|
954.29
|
54
|
1014.80
|
1008.98
|
55
|
1048.40
|
1053.77
|
56
|
1090.85
|
1108.56
|
57
|
1135.33
|
1152.28
|
58
|
1206.31
|
1192.35
|
59
|
1249.34
|
1245.93
|
> plot(bnkwh$actualbnkwh,bnkwh$fittedbnkwh, xlab="actual bnkwh", ylab="fitted bnkwh", type="p",
pch=20, col=4)
> abline(0,1, col=2)
Figure 2 actual
vs fitted bnkwh
> rmse<-sqrt(sum((bnkwh$actual-bnkwh$fitted)^2)/nrow(bnkwh))
> rmse
[1]
10.47169
The actual
bnkwh versus predicted bnkwh
scatter has been plotted in order to understand the model fit. The scatter plot
has been shown in Figure 2.
The forecast
has been done for bnkwh for the next 10 years. The new
data for regressor variables has been estimated by
making use of arima model. In fact, auto.arima function of the 'forecast' package has been used
for making the estimation of gross domestic product in billion rupees and
population in million.
> #arima prediction of 'popmn' for
next ten years
> library(forecast)
> auto.arima(scaledata$pop_mn)
Series: scaledata$pop_mn
ARIMA(0,2,1)
Coefficients:
ma1
-0.8907
s.e. 0.0551
sigma^2 estimated as 7.012e-05: log likelihood=191.45
AIC=-378.89 AICc=-378.67 BIC=-374.81
>
fit2<-arima(scaledata$pop_mn,
order=c(0,2,1))
> fit2
Call:
arima(x =
scaledata$pop_mn, order = c(0, 2, 1))
Coefficients:
ma1
-0.8907
s.e. 0.0551
sigma^2 estimated as 6.889e-05: log likelihood = 191.45, aic = -378.89
>
fpre2<-predict(fit2, n.ahead=10)
> fprepopmn<-fpre2$pred
> fprepopmn
Time
Series:
Start = 60
End = 69
Frequency = 1
[1] 1.021688 1.043377 1.065065 1.086754
1.108442 1.130131 1.151819 1.173508
[9] 1.195196 1.216885
> #arima prediction of 'gdpbn' for
next ten years
> library(forecast)
> auto.arima(scaledata$gdp_bn)
Series: scaledata$gdp_bn
ARIMA(1,2,1)
Coefficients:
ar1
ma1
0.9820 -0.8670
s.e. 0.0287
0.0836
sigma^2 estimated as 5.574e-05: log likelihood=198.83
AIC=-391.67 AICc=-391.22 BIC=-385.54
>
fit3<-arima(scaledata$gdp_bn,
order=c(1,2,1))
> fit3
Call:
arima(x =
scaledata$gdp_bn, order = c(1, 2, 1))
Coefficients:
ar1
ma1
0.9820 -0.8670
s.e. 0.0287
0.0836
sigma^2 estimated as 5.378e-05: log likelihood = 198.83, aic = -391.67
>
fpre3<-predict(fit3, n.ahead=10)
> fpregdpbn<-fpre3$pred
> fpregdpbn
Time
Series:
Start = 60
End = 69
Frequency = 1
[1] 1.133588 1.275175 1.424617 1.581772
1.746503 1.918672 2.098146 2.284793
[9] 2.478485 2.679094
> futuredf<-data.frame(pop_mn=fprepopmn, gdp_bn=fpregdpbn)
> futbnkwh<-predict(kwh_nn,futuredf)
> bnkwhfuture<-futbnkwh*(max(kwhgdp$bn_kwh)-min(kwhgdp$bn_kwh))+min(kwhgdp$bn_kwh)
> bnkwhfuture
[,1]
1 1295.468
2 1340.575
3 1381.663
4 1419.304
5 1454.158
6 1486.896
7 1518.160
8 1548.522
9 1578.469
10 1608.398
> fittedbnkwh<-ts(bnkwh$fittedbnkwh,start=1)
> futurebnkwh<-ts(bnkwhfuture,start=60)
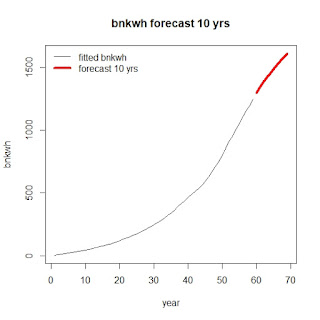
> ts.plot(fittedbnkwh, futurebnkwh, type="l", col=c(1,2), lwd=c(1,4), xlab="year", ylab="bnkwh", main="bnkwh forecast 10 yrs")
>
legend("topleft", lty=c(1,1), col=c(1,2), lwd=c(1,4), legend=c("fitted bnkwh","forecast 10 yrs"),bty="n")
Figure 3
forecast of bnkwh for next 10 years
> #R
code:
> abc <- read.csv("bnkwh_gdp.csv",
sep=",", header=TRUE)
> kwhgdp<-data.frame(abc[,c(2,3,5)])
> scalemin<-apply(kwhgdp,2,min)
> scalemax<-apply(kwhgdp,2,max)
> scaledata<-data.frame(scale(kwhgdp, center=scalemin, scale=scalemax-scalemin))
> scaledata
pop_mn
|
gdp_bn
|
bn_kwh
| |
1
|
0.000000000
|
0.000000000
|
0.000000000
|
2
|
0.010695190
|
0.000054865
|
0.002604674
|
3
|
0.021390370
|
0.000129054
|
0.005209348
|
4
|
0.032085560
|
0.000288541
|
0.007814021
|
5
|
0.042780750
|
0.000492415
|
0.010418695
|
6
|
0.054545450
|
0.000569868
|
0.013023369
|
7
|
0.065240640
|
0.000767107
|
0.016934437
|
8
|
0.077005350
|
0.001060071
|
0.020837390
|
9
|
0.089839570
|
0.001178751
|
0.024740344
|
10
|
0.101604280
|
0.001393419
|
0.028140214
|
11
|
0.114438500
|
0.001552433
|
0.031531970
|
12
|
0.128342250
|
0.001729032
|
0.034477442
|
13
|
0.142245990
|
0.002003040
|
0.037422915
|
14
|
0.156149730
|
0.002644516
|
0.040368387
|
15
|
0.170053480
|
0.003296576
|
0.045439792
|
16
|
0.185026740
|
0.003611075
|
0.050519312
|
17
|
0.198930480
|
0.003965801
|
0.055469004
|
18
|
0.213903740
|
0.004620072
|
0.060418695
|
19
|
0.228877010
|
0.005087423
|
0.069441740
|
20
|
0.245989300
|
0.005687198
|
0.071210646
|
21
|
0.262032090
|
0.006956408
|
0.084274586
|
22
|
0.275935830
|
0.008317919
|
0.085329438
|
23
|
0.293048130
|
0.009379675
|
0.091983122
|
24
|
0.309090910
|
0.011068110
|
0.100016228
|
25
|
0.326203210
|
0.012495540
|
0.113534567
|
26
|
0.343315510
|
0.014228260
|
0.124521259
|
27
|
0.360427810
|
0.016021060
|
0.138558909
|
28
|
0.378609630
|
0.018308740
|
0.150243427
|
29
|
0.396791440
|
0.021826250
|
0.165903927
|
30
|
0.414973260
|
0.025185540
|
0.185410581
|
31
|
0.433155080
|
0.029527860
|
0.200714054
|
32
|
0.451336900
|
0.034010300
|
0.219157741
|
33
|
0.468449200
|
0.039228350
|
0.230817916
|
34
|
0.489839570
|
0.045355890
|
0.249156118
|
35
|
0.509090910
|
0.053424080
|
0.270577735
|
36
|
0.528342250
|
0.062940330
|
0.294595910
|
37
|
0.547593580
|
0.073100020
|
0.307489451
|
38
|
0.566844920
|
0.081155670
|
0.328432327
|
39
|
0.587165780
|
0.093224930
|
0.350178513
|
40
|
0.606417110
|
0.104771200
|
0.376306394
|
41
|
0.625668450
|
0.112510300
|
0.391561181
|
42
|
0.648128340
|
0.122045700
|
0.406118143
|
43
|
0.665240640
|
0.131726500
|
0.418500487
|
44
|
0.682352940
|
0.147583500
|
0.444790652
|
45
|
0.700534760
|
0.168594300
|
0.468565401
|
46
|
0.718716580
|
0.192152400
|
0.492421292
|
47
|
0.735828880
|
0.223440000
|
0.530436547
|
48
|
0.752941180
|
0.260566200
|
0.572914638
|
49
|
0.770053480
|
0.293767500
|
0.587682571
|
50
|
0.787165780
|
0.338137800
|
0.635232068
|
51
|
0.804278070
|
0.404611700
|
0.671746186
|
52
|
0.821390370
|
0.469406100
|
0.735361895
|
53
|
0.837433160
|
0.516883100
|
0.768873742
|
54
|
0.860962570
|
0.585242800
|
0.809688413
|
55
|
0.877005350
|
0.648842500
|
0.836952288
|
56
|
0.951871660
|
0.711072700
|
0.871397274
|
57
|
0.979679140
|
0.788549700
|
0.907489451
|
58
|
0.983957220
|
0.874557800
|
0.965084388
|
59
|
1.000000000
|
1.000000000
|
1.000000000
|
> nnpredlevel<-numeric(nrow(kwhgdp))
>
i<-integer(nrow(kwhgdp))
> xyz<-numeric(nrow(kwhgdp))
> library(nnet)
> for (j in 1:5){
+ for (i in 1:nrow(kwhgdp)) {
+ nntest<-as.data.frame(scaledata[i,c(1:2)]);
+ nntrain<-as.data.frame(scaledata[-i,]);
+ nnfit<-nnet(bn_kwh~gdp_bn+pop_mn,
data=nntrain, size = 4, decay = 1e-3, linout = T, skip = F, maxit =
1000, Hess = T);
+ nnpred<-predict(nnfit, nntest);
+ nnpredlevel[i]<-nnpred[,1]*(max(kwhgdp$bn_kwh)-min(kwhgdp$bn_kwh))+min(kwhgdp$bn_kwh);
+ }
+ nnpredlevel
+ xyz<-cbind(xyz,nnpredlevel)
+ }
# weights: 17
initial value
6.315430
iter 10 value 0.043400
iter 20 value 0.029248
iter 30 value 0.026542
iter 40 value 0.025696
iter 50 value 0.024177
iter 60 value 0.022226
iter 70 value 0.021287
iter 80 value 0.020766
iter 90 value 0.020102
iter 100 value 0.019594
iter 110 value 0.019382
iter 120 value 0.019246
iter 130 value 0.019207
iter 140 value 0.019160
final value 0.019156
converged
........................
........................
# weights: 17
initial value
5.533753
iter 10 value 0.041560
iter 20 value 0.027292
iter 30 value 0.022990
iter 40 value 0.022279
iter 50 value 0.020596
iter 60 value 0.020322
iter 70 value 0.020144
iter 80 value 0.019869
iter 90 value 0.019411
iter 100 value 0.019302
iter 110 value 0.019168
iter 120 value 0.019069
iter 130 value 0.019016
iter 140 value 0.018898
iter 150 value 0.018871
iter 160 value 0.018856
iter 170 value 0.018841
iter 180 value 0.018836
iter 190 value 0.018836
iter 200 value 0.018835
iter 210 value 0.018835
iter 210 value 0.018835
iter 210 value 0.018835
final value 0.018835
converged
> xyz<-xyz[,-1]
> xyz
nnpredlevel
|
nnpredlevel
|
nnpredlevel
|
nnpredlevel
|
nnpredlevel
| |
[1,]
|
1.58957
|
1.55163
|
2.56679
|
2.30885
|
2.30784
|
[2,]
|
6.43988
|
6.62874
|
6.62314
|
6.62513
|
6.64721
|
[3,]
|
9.71847
|
10.62948
|
10.74662
|
9.69312
|
9.61503
|
[4,]
|
14.82322
|
15.00188
|
14.99733
|
15.01592
|
15.00666
|
[5,]
|
19.07408
|
19.18885
|
18.90062
|
19.15793
|
19.33661
|
[6,]
|
23.94919
|
23.96592
|
23.97387
|
24.08500
|
24.07630
|
[7,]
|
28.18760
|
28.15781
|
28.46859
|
28.31568
|
28.27585
|
[8,]
|
33.44738
|
33.44921
|
33.00205
|
33.44350
|
33.44299
|
[9,]
|
38.92595
|
38.83271
|
38.92320
|
38.82727
|
38.74279
|
[10,]
|
44.06365
|
43.88326
|
43.88333
|
44.08312
|
44.16110
|
[11,]
|
49.91590
|
49.91425
|
49.91044
|
49.98102
|
49.91191
|
[12,]
|
56.46960
|
56.43642
|
56.50409
|
56.41474
|
56.45001
|
[13,]
|
63.29158
|
63.25680
|
63.29091
|
63.28935
|
63.28870
|
[14,]
|
70.53290
|
70.62891
|
70.56593
|
70.56338
|
70.53200
|
[15,]
|
77.95662
|
77.92560
|
77.95076
|
77.95345
|
77.93343
|
[16,]
|
85.84820
|
85.85527
|
85.85935
|
85.87881
|
85.85206
|
[17,]
|
93.45821
|
93.44594
|
93.45316
|
93.46559
|
93.46716
|
[18,]
|
102.11145
|
102.10886
|
102.11007
|
102.54864
|
102.14915
|
[19,]
|
110.59833
|
110.59555
|
110.59997
|
110.56891
|
110.59417
|
[20,]
|
121.23660
|
121.61360
|
121.70392
|
121.27454
|
121.70670
|
[21,]
|
131.24988
|
131.21871
|
131.31531
|
131.73250
|
131.35157
|
[22,]
|
141.10263
|
141.21363
|
141.09433
|
141.07734
|
141.21715
|
[23,]
|
152.73168
|
152.63379
|
152.61030
|
152.73015
|
152.77698
|
[24,]
|
164.26882
|
164.12910
|
164.29025
|
164.11859
|
164.27865
|
[25,]
|
176.08491
|
175.95818
|
175.94175
|
175.95531
|
175.96007
|
[26,]
|
188.53274
|
188.50408
|
188.52275
|
188.50122
|
189.16077
|
[27,]
|
201.17042
|
201.17659
|
201.23813
|
201.19003
|
201.16410
|
[28,]
|
215.64350
|
216.22863
|
216.16810
|
215.48488
|
215.66654
|
[29,]
|
231.07762
|
231.61952
|
230.95694
|
231.55786
|
230.97177
|
[30,]
|
246.67414
|
246.32361
|
246.47803
|
246.46893
|
246.29091
|
[31,]
|
263.32476
|
263.16945
|
263.69472
|
263.16948
|
263.33151
|
[32,]
|
280.76281
|
280.36990
|
280.20359
|
280.74955
|
280.75567
|
[33,]
|
297.93349
|
298.21802
|
297.75515
|
297.93394
|
297.94592
|
[34,]
|
319.35426
|
319.35965
|
319.35887
|
319.52706
|
319.52437
|
[35,]
|
341.28680
|
341.14967
|
341.33656
|
341.33260
|
341.27332
|
[36,]
|
364.54507
|
364.34365
|
364.55115
|
364.34425
|
364.55196
|
[37,]
|
388.97786
|
389.18608
|
388.98846
|
389.21046
|
389.11537
|
[38,]
|
411.38960
|
411.34063
|
411.38285
|
411.38978
|
411.19927
|
[39,]
|
438.30897
|
438.17416
|
438.33524
|
438.33485
|
438.30050
|
[40,]
|
463.39167
|
463.51106
|
463.47021
|
463.50214
|
463.50851
|
[41,]
|
485.63055
|
485.65473
|
485.65733
|
485.64532
|
485.37044
|
[42,]
|
512.41138
|
512.24379
|
512.42736
|
512.37029
|
512.41245
|
[43,]
|
534.79987
|
535.09469
|
534.48602
|
534.83334
|
535.11134
|
[44,]
|
561.59164
|
561.82022
|
561.96304
|
561.23602
|
561.57539
|
[45,]
|
594.68838
|
594.53861
|
594.46595
|
594.30110
|
594.28840
|
[46,]
|
629.28624
|
628.83513
|
629.28136
|
628.85261
|
629.29305
|
[47,]
|
667.45192
|
667.47399
|
667.83344
|
667.46820
|
667.44984
|
[48,]
|
710.24060
|
709.96835
|
710.22699
|
710.24750
|
709.63679
|
[49,]
|
750.78032
|
750.77388
|
750.50283
|
750.54439
|
750.24516
|
[50,]
|
795.71646
|
795.72035
|
795.71928
|
795.68897
|
795.71289
|
[51,]
|
858.99474
|
859.05731
|
858.85386
|
859.01969
|
858.85236
|
[52,]
|
911.46829
|
911.48475
|
911.49773
|
911.46998
|
911.43589
|
[53,]
|
952.40475
|
951.85585
|
951.83765
|
952.24540
|
952.39766
|
[54,]
|
1007.42668
|
1007.41415
|
1007.95004
|
1007.42758
|
1007.38508
|
[55,]
|
1054.11776
|
1054.89923
|
1054.10224
|
1054.44394
|
1054.79159
|
[56,]
|
1113.96599
|
1113.95926
|
1113.96968
|
1113.95371
|
1113.94464
|
[57,]
|
1156.98654
|
1156.93427
|
1159.00238
|
1157.03444
|
1158.92111
|
[58,]
|
1187.83263
|
1187.69251
|
1187.68199
|
1187.68081
|
1187.91383
|
[59,]
|
1242.30081
|
1239.65328
|
1239.66389
|
1239.60043
|
1239.62384
|
> result<-rowMeans(xyz)
> result
[1]
|
2.0649
|
6.5928
|
10.0805
|
14.9690
|
19.1316
|
24.0101
|
[7]
|
28.2811
|
33.3570
|
38.8504
|
44.0149
|
49.9267
|
56.4550
|
[13]
|
63.2835
|
70.5646
|
77.9440
|
85.8587
|
93.4580
|
102.2056
|
[19]
|
110.5914
|
121.5071
|
131.3736
|
141.1410
|
152.6966
|
164.2171
|
[25]
|
175.9800
|
188.6443
|
201.1879
|
215.8383
|
231.2367
|
246.4471
|
[31]
|
263.3380
|
280.5683
|
297.9573
|
319.4248
|
341.2758
|
364.4672
|
[37]
|
389.0956
|
411.3404
|
438.2907
|
463.4767
|
485.5917
|
512.3731
|
[43]
|
534.8651
|
561.6373
|
594.4565
|
629.1097
|
667.5355
|
710.0640
|
[49]
|
750.5693
|
795.7116
|
858.9556
|
911.4713
|
952.1483
|
1007.5207
|
[55]
|
1054.4710
|
1113.9587
|
1157.7757
|
1187.7604
|
1240.1684
|
> resultdf<-data.frame(actualbnkwh=kwhgdp$bn_kwh, predbnkwh=result)
> resultdf
actualbnkwh
|
predbnkwh
| |
1
|
16.94
|
2.06
|
2
|
20.15
|
6.59
|
3
|
23.36
|
10.08
|
4
|
26.57
|
14.97
|
5
|
29.78
|
19.13
|
6
|
32.99
|
24.01
|
7
|
37.81
|
28.28
|
8
|
42.62
|
33.36
|
9
|
47.43
|
38.85
|
10
|
51.62
|
44.01
|
11
|
55.80
|
49.93
|
12
|
59.43
|
56.45
|
13
|
63.06
|
63.28
|
14
|
66.69
|
70.56
|
15
|
72.94
|
77.94
|
16
|
79.20
|
85.86
|
17
|
85.30
|
93.46
|
18
|
91.40
|
102.21
|
19
|
102.52
|
110.59
|
20
|
104.70
|
121.51
|
21
|
120.80
|
131.37
|
22
|
122.10
|
141.14
|
23
|
130.30
|
152.70
|
24
|
140.20
|
164.22
|
25
|
156.86
|
175.98
|
26
|
170.40
|
188.64
|
27
|
187.70
|
201.19
|
28
|
202.10
|
215.84
|
29
|
221.40
|
231.24
|
30
|
245.44
|
246.45
|
31
|
264.30
|
263.34
|
32
|
287.03
|
280.57
|
33
|
301.40
|
297.96
|
34
|
324.00
|
319.42
|
35
|
350.40
|
341.28
|
36
|
380.00
|
364.47
|
37
|
395.89
|
389.10
|
38
|
421.70
|
411.34
|
39
|
448.50
|
438.29
|
40
|
480.70
|
463.48
|
41
|
499.50
|
485.59
|
42
|
517.44
|
512.37
|
43
|
532.70
|
534.87
|
44
|
565.10
|
561.64
|
45
|
594.40
|
594.46
|
46
|
623.80
|
629.11
|
47
|
670.65
|
667.54
|
48
|
723.00
|
710.06
|
49
|
741.20
|
750.57
|
50
|
799.80
|
795.71
|
51
|
844.80
|
858.96
|
52
|
923.20
|
911.47
|
53
|
964.50
|
952.15
|
54
|
1014.80
|
1007.52
|
55
|
1048.40
|
1054.47
|
56
|
1090.85
|
1113.96
|
57
|
1135.33
|
1157.78
|
58
|
1206.31
|
1187.76
|
59
|
1249.34
|
1240.17
|
Figure 4 actual
bnkwh versus predicted bnkwh
> plot(resultdf$actualbnkwh, resultdf$predbnkwh, pch=16, col=4,
xlab="actual bnkwh", ylab="predicted bnkwh",
main="Leave-one-out cross validation")
> abline(0,1,col=2)
> rmse<-sqrt(sum((resultdf$actualbnkwh-resultdf$predbnkwh)^2)/nrow(resultdf))
> rmse
[1]
11.74785
The author can
be reached at: arg1962@gmail.com mobile: 9488361726






Comments
Post a Comment